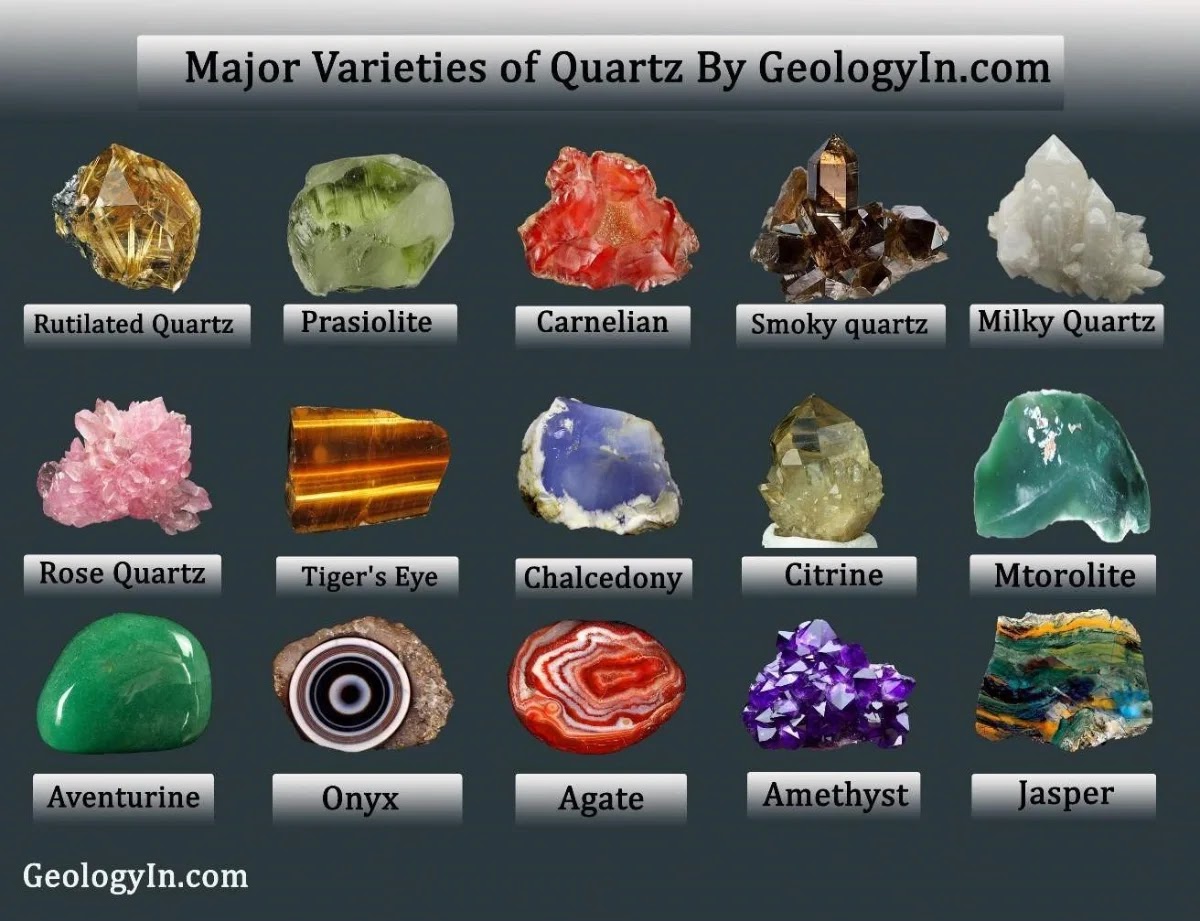
Garden Quartz: Properties, Uses, Occurrence
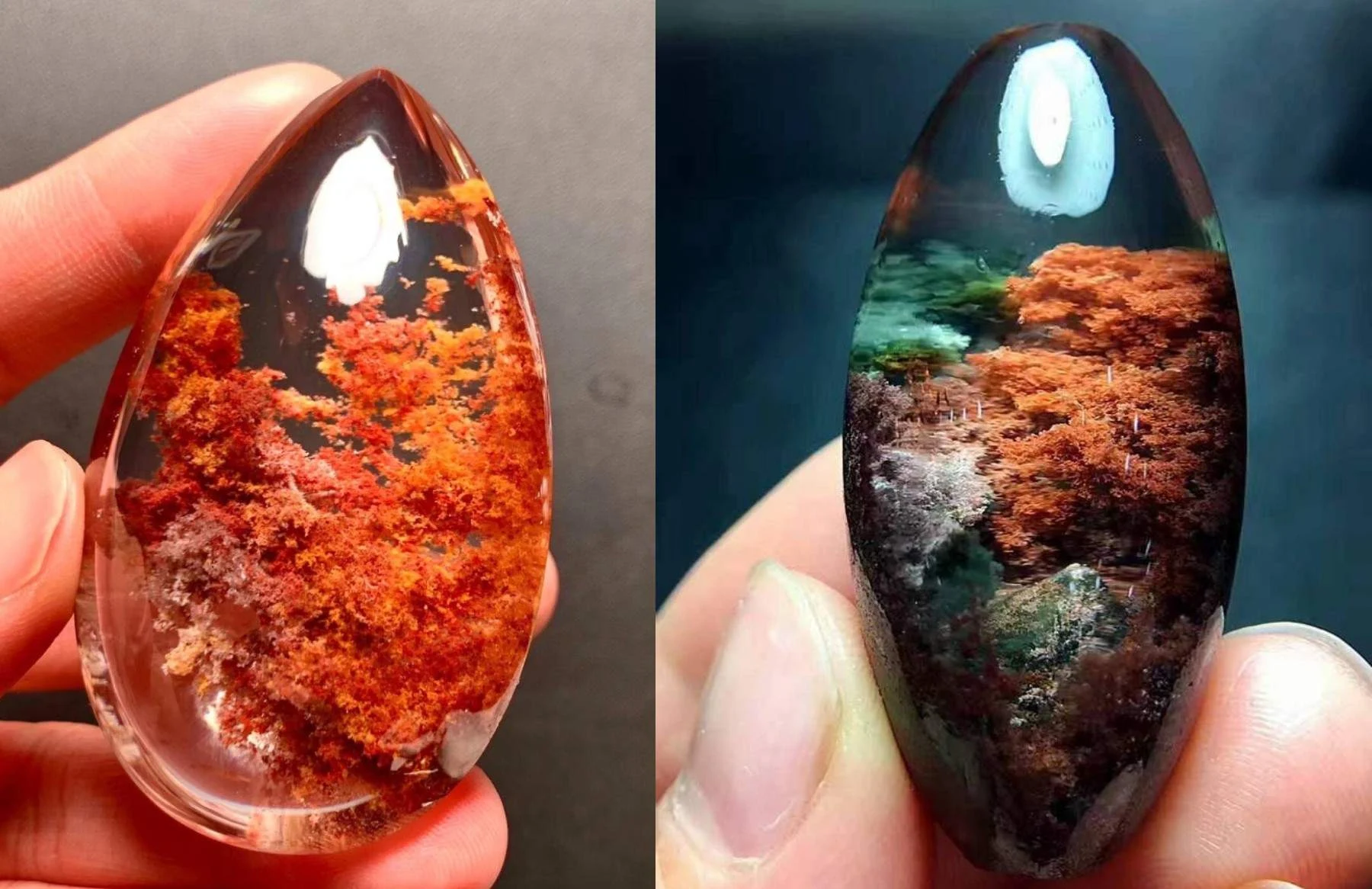
Garden Quartz is a variety of quartz containing mesmerizing mineral inclusions that resemble miniature landscapes within the stone. These inclusions, primarily composed of chlorite, hematite, and feldspar, create intricate patterns that mimic moss, ferns, clouds, and even mountains, trapped in a frozen moment of the crystal's formation.
Garden Quartz, also known as lodolite, boasts a unique world of miniature landscapes trapped inside its crystal structure.
How is Garden Quartz Formed
The formation of garden quartz occurs during the crystallization of silica-rich fluids within fractures and cavities in rock formations. Its formation involves two stages:
Quartz Crystallization: Silica-rich fluids slowly deposit within cavities or fractures in rocks, gradually forming clear quartz crystals.
Inclusion Entrapment: During crystal growth, other minerals like chlorite, hematite, and feldspar get trapped within the growing quartz. These inclusions arrange themselves in unique patterns, resembling landscapes, gardens, or even otherworldly scenes.
Garden Quartz Properties
Composition: Garden Quartz is a variety of quartz, a naturally occurring mineral with the chemical formula SiO₂. However, it's not pure silica; it contains inclusions of various other minerals, primarily chlorite, hematite, and feldspar. These inclusions are responsible for the gemstone's captivating landscapes and unique properties.
Color: Garden Quartz boasts a stunning range of colors thanks to its diverse inclusions. The base quartz can be transparent, milky white, or even smoky gray, while the inclusions add shades of green, brown, red, black, and even gold. The interplay of these colors creates mesmerizing miniature landscapes within the crystal, earning it nicknames like "lodolite" and "landscape quartz."
Luster: Garden Quartz typically displays a vitreous luster, meaning it has a glassy and shiny appearance. However, the luster can vary depending on the specific inclusions and the overall polish of the stone. Some inclusions, like chlorite, may have a slightly matte or greasy luster that contrasts with the quartz's brilliance.
Crystal System: Like all quartz varieties, Garden Quartz belongs to the trigonal crystal system. This means its crystals grow in six-sided prisms with pointed terminations.
Streak: When scratched, Garden Quartz leaves a white streak, similar to other quartz varieties. This is because the hardness of the inclusions is generally comparable to that of quartz.
Hardness: Garden Quartz is a relatively hard gemstone, measuring 7 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. This means it can scratch most other minerals except for diamond, corundum, and other harder gemstones.
Cleavage: Garden Quartz has no distinct cleavage, meaning it doesn't break along preferred planes. However, it can fracture conchoidally, meaning the fracture pattern resembles the ripples on a seashell.
Crystal Form: As mentioned earlier, Garden Quartz rarely forms perfect hexagonal crystals. It's more commonly found as rounded masses, clusters, or in botryoidal (grape-like) formations.
Density: The density of Garden Quartz can vary slightly depending on the specific inclusions, but it typically ranges from 2.60 to 2.65 g/cm³. This is slightly heavier than pure quartz (2.65 g/cm³) due to the denser mineral inclusions.
Transparency: The transparency of Garden Quartz can also vary. Some stones may be completely transparent, allowing the inclusions to be clearly seen, while others may be partially translucent or opaque due to the presence of more abundant inclusions or milky quartz.
Fracture: As mentioned earlier, Garden Quartz can fracture conchoidally, meaning the fractures are irregular and resemble the ripples on a seashell. This can be a concern when cutting or polishing the gemstone, as it can create chips or cracks.
Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of Garden Quartz is slightly higher than its density due to the influence of air pockets within the stone. It typically ranges from 2.63 to 2.68.
Solubility: Garden Quartz is highly insoluble in water and most common acids. However, it may be slightly affected by strong hydrofluoric acid.
Magnetism: Garden Quartz is not magnetic.
Fluorescence: Some Garden Quartz specimens, particularly those with inclusions of rutile, may exhibit weak fluorescence under longwave ultraviolet light. This fluorescence can appear orange, yellow, or white.
Pleochroism: Pleochroism refers to the change in color a gemstone exhibits when viewed from different angles. While some quartz varieties can display weak pleochroism, Garden Quartz generally does not.
Refractive Index: The refractive index of Garden Quartz is typically around 1.54 to 1.55, similar to other quartz varieties. This value can vary slightly depending on the specific inclusions and the orientation of the crystal.
Inclusions: The inclusions are the heart and soul of Garden Quartz, creating its unique beauty and contributing to its metaphysical properties. The most common inclusions are:
- Chlorite: Responsible for the green mossy and fern-like patterns.
- Hematite: Creates red and brown needle-like inclusions or golden-red patches.
- Feldspar: Can appear as white, yellow, or brown inclusions.
- Rutile: Rare, but can create golden needle-like inclusions that fluoresce under ultraviolet light.
These inclusions tell a story within the crystal, capturing the journey of its formation and adding a touch of magic to its appearance.
Where is Garden Quartz Found
Garden quartz is primarily found in the Minas Gerais region of Brazil. This region boasts several mines where Garden Quartz is extracted, particularly in the municipalities of Teofilo Otoni, Diamantina, and Sao Jose da Safira.
Secondary Sources:
Madagascar: Some Garden Quartz crystals have been discovered in Madagascar, although they may be less common and have slightly different characteristics compared to Brazilian stones.
Kazakhstan: Certain deposits in Kazakhstan are known to yield Garden Quartz, though they might be more challenging to find due to limited commercial availability.
United States: Rare occurrences of Garden Quartz have been reported in various locations across the US, including North Carolina, Colorado, and California. However, these findings are typically sporadic and not commercially viable.
 |
| Garden Quartz crystal |
Garden Quartz Vs Phantom Quartz
Garden Quartz
Refers to clear quartz containing various mineral inclusions, creating the appearance of miniature landscapes within the stone. These inclusions can be green (chlorite), red (hematite), brown (rutile), white (feldspar), etc.
Phantom Quartz
A more general term for any quartz crystal containing internal, transparent or semi-transparent shapes that resemble earlier stages of its growth. These "phantoms" are the result of the crystal stopping and restarting its growth multiple times.
So, all garden quartz are phantom quartz due to the "phantom" effect of the inclusions. However, not all phantom quartz are garden quartz, as they might not have the diverse mineral inclusions that create the "garden" appearance.
 |
| Garden Quartz |
Garden Quartz Uses
Jewelry and Decoration
Jewelry: Exquisitely crafted into rings, pendants, bracelets, and earrings, Garden Quartz adds a touch of nature's magic to personal adornment. Its mesmerizing inclusions make it a unique and captivating conversation starter.
Home Decor: Introduce serenity and beauty into your living space with Garden Quartz sculptures, spheres, clusters, or tumbled stones. Its vibrant landscapes can elevate any decor style and create a peaceful atmosphere.
Gifts: A meaningful and cherished gift for loved ones seeking spiritual growth, emotional healing, or a touch of natural wonder in their lives.
 |
| Garden Quartz |
Metaphysical Uses
Spiritual Growth: Believed to connect with higher realms, activate psychic abilities, and facilitate spiritual growth. Garden Quartz can aid in meditation, enhance intuition, and provide guidance on one's spiritual path.
Emotional Healing: Its gentle energy helps heal past traumas, alleviate stress and anxiety, and promote emotional clarity. It can foster inner peace, self-acceptance, and release blockages to emotional well-being.
Manifestation: Its amplifying properties are believed to attract abundance, prosperity, and desired outcomes. Holding or meditating with Garden Quartz can empower one to set intentions and manifest their dreams.
 |
| Garden Quartz |
Crystal Healing
Physical Healing: Believed to strengthen the immune system, detoxify the body, and reduce pain. It can support cellular regeneration, boost energy levels, and offer gentle healing support.
Chakra Balancing: Aligns and balances all chakras, particularly the Crown and Heart chakras. This promotes harmony, spiritual awareness, and emotional balance within the energy centers.
Protection: Its grounding energy offers protection from negativity, harmful energies, and psychic attacks. Garden Quartz can create a safe and uplifting space for personal growth and transformation.
 |
| Garden Quartz cab |
Conclusion
Garden quartz is a fascinating geological phenomenon that offers a captivating blend of scientific intrigue and potential metaphysical properties. While its scientific explanation for its alleged healing and spiritual effects remains elusive, its undeniable beauty and unique composition continue to captivate collectors, artists, and those seeking a connection to the natural world and the mysteries it holds.
See also:
Chevron Amethyst - Properties, Uses, Occurrence
Rutile Quartz - Types, Formation, Colors, Uses
Blue Quartz - Formation, Types, Properties, Occurrence




%20(1).webp)